A new paper investigates how transmission power can be adaptively controlled in Bluetooth Low Energy communications to improve reliability while reducing energy consumption in dynamic Internet of Things environments. It focuses on the complex relationship between received signal strength, data throughput, transmission power and overall system power consumption, all of which are strongly influenced by environmental variability such as interference, distance and multipath effects.
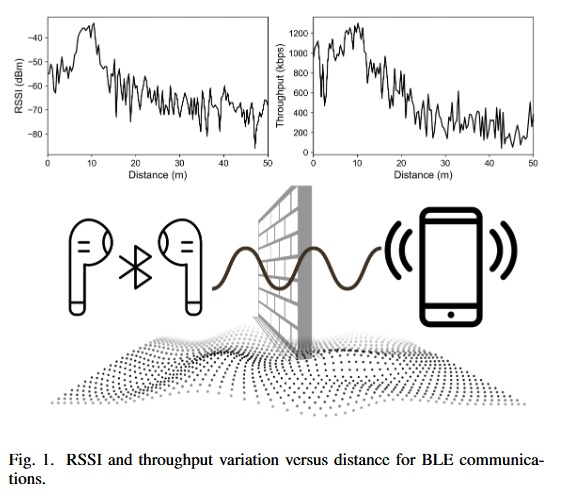
The authors first provide an extensive experimental analysis using Nordic BLE hardware to characterise how changes in transmission power affect signal strength, throughput and energy use across clean, moderately complex and highly noisy environments. The results show that increasing transmission power generally improves both RSSI and throughput, but at a significant energy cost, particularly when a front-end power amplifier is used. They also demonstrate that RSSI can be measured reliably at high update rates, whereas throughput measurements become increasingly noisy at high calculation frequencies due to the packet-based nature of BLE.
Building on these observations, the paper proposes a closed-loop transmission power control framework based on proportional–integral–derivative controllers implemented on the central device. Three strategies are developed and evaluated. The RSSI-based controller responds quickly to signal fluctuations and works well in clean or fast-changing environments, but it does not directly guarantee a desired data rate. The throughput-based controller directly targets application-level performance and performs better in complex environments, but its slower response and higher variability make it vulnerable to sudden disturbances.
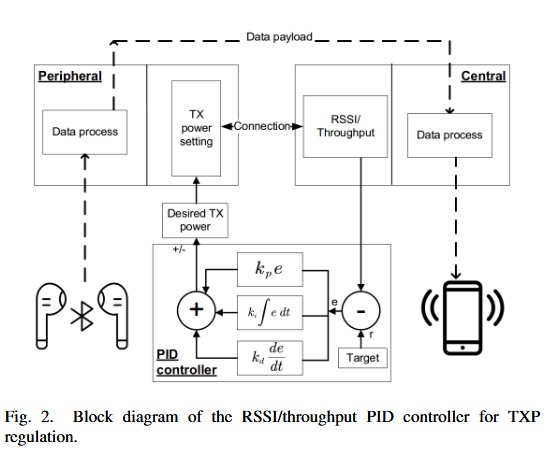
To overcome the limitations of both approaches, the authors introduce a hybrid dual-loop controller that combines throughput-based control with fast RSSI regulation. In this design, the throughput loop sets an appropriate RSSI target, while a faster RSSI loop adjusts transmission power to maintain that target. Experimental results show that this hybrid method achieves more stable throughput with lower variance, maintains connectivity during abrupt signal degradation and delivers substantial energy savings compared with fixed maximum transmission power.
The study concludes that closed-loop, PID-based transmission power control is an effective way to balance reliability and energy efficiency in BLE systems. Among the evaluated strategies, the hybrid RSSI–throughput approach provides the best overall performance in dynamic and complex environments. Future work is proposed on extending the framework to multi-node and mesh networks and on using adaptive or learning-based techniques to further improve controller performance under mobility and varying traffic conditions.