Minew have recently added a video showing how to change the battery in the D15N:
Author: Support
Bluetooth Low Energy in Noisy RF Environments
Michael Spork, Carlo Alberto Boano and Kay Romer of the Institute for Technical Informatics, Graz University of Technology, Austria have a recent paper on Improving the Timeliness of Bluetooth Low Energy in Noisy RF Environments.
The paper looks into the affect of radio frequency (RF) noise on connection based Bluetooth LE communication and provides a mechanism that significantly improves the time taken to send a message in noisy environments. To be clear, beacon-related scenarios rarely use GATT connection based communication and instead use connection-less communication repeatedly broadcasting short packets on 3 advertisement channels (37, 38, and 39). Connection tends to be used only to set up beacon parameters or for more advanced scenarios where a device such as a smartphone connects to the beacon for bidirectional data transfer to get real time data, for example, more timely motion detection.
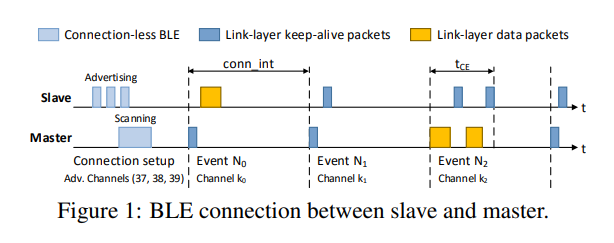
The authors distinguish their research as experimentally derived as opposed to analytic (just using calculations). They show how the Bluetooth Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH) algorithm allows Bluetooth devices to blacklist interfered channels and re-transmit packets on different frequencies until interference is avoided.
The paper shows how the AFH algorithm mitigates the effects of Wi-Fi interference near a Bluetooth master by blacklisting channels. An interesting insight is that the master is unable to detect Wi-Fi interference near the Bluetooth slave and is unable to adapt resulting in UDP messages being significantly delayed.
“Our experiments show that BLE connections are eventually able to successfully transmit all data packets, even under heavy Wi-Fi or Bluetooth interference”
The authors demonstrate that by lowering the connection interval in response to changes in the link quality, an application can reduced the average number of packets delayed from 6.18% to 0.54%.
Read about Bluetooth LE on the Factory Floor
Graphical Bluetooth Analyser for Linux
Sparrow is an open source Graphical Bluetooth and WiFi Analyzer for Linux. It provides a 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz spectrum view, listens for Bluetooth LE advertising and tracks advertisement or iBeacons advertisement sources. It can also be used to advertise iBeacon.
Sparrow is useful for advanced users who need to diagnose more advanced problems related to interference or which part of a system isn’t working.
Beacons for Motion Sensing
One of our customers, Activ84Health in Belgium, has an interesting product that we have been working on, Memoride, that encourages the use of cycling fitness machines through the use of a moving map and visual route.
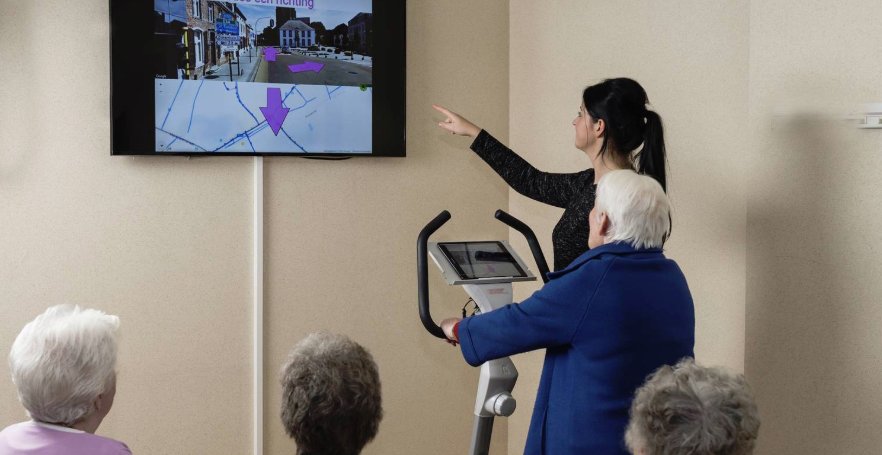

The system uses beacons to detect movement of the cycling machine.
The technology is featured in the Care England Best Practice Report:
Beacons Inside Products
Products are increasing including iBeacon or more generic Bluetooth LE advertising in order to identify themselves to apps. There’s the recent example of the Tesla 3.
Higher end WiFi access points such as the mesh Linksys VELOP also use Bluetooth for identification in mobile apps. Recently we came across a new wireless security system, AJAX, that also uses iBeacon for identification to apps:

Bluetooth advertising provides a solution to the ‘chicken and egg’ problem of how to connect to a product to set it up, before it has been set up and connected to a (usually WiFi) network.
Using Bluetooth Beacons for Jungle Vehicle Poacher Tracking
There’s new research by Karan Juj and Charith Perera of Cardiff University on Exploring the Suitability of BLE Beacons to Track Poacher Vehicles in Harsh Jungle Terrains (pdf). The paper describes a real world study conducted in a Malaysian jungle that tracks poacher vehicles.
Deep jungle terrain has challenges because GPS doesn’t work, there’s no cellular connection and 100% humidity can hinder wireless signal.
The study mounted Bluetooth beacons beside a road and placed a concealed receiver inside a vehicle:
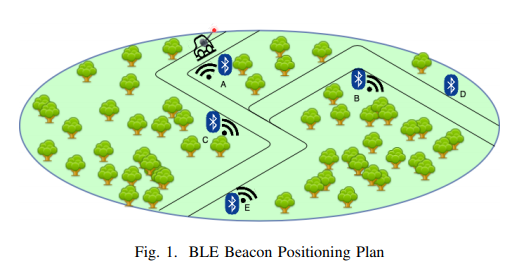

The researchers tested various types of obstructions that would be faced in deployment and measured the reliability of detecting beacons from under bonnet:

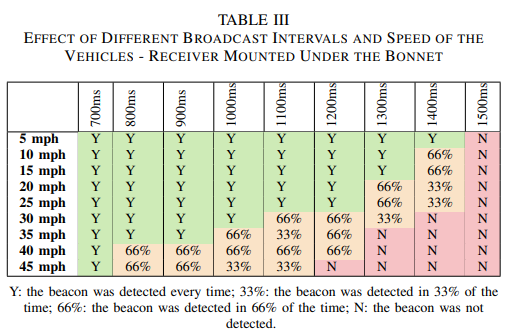
After extensive evaluation, the researchers found that Bluetooth LE beacons can be successfully used in jungle terrains to a track vehicle.
What is Bluetooth Beacon Technology?
Bluetooth beacons use Bluetooth LE, a low power version of Bluetooth to repeatedly send out a short amount of data typically up to 50m but in some cases hundreds of metres. The data usually includes an identifier in various standard formats such as iBeacon or Eddystone. It can also include sensor data.
The beacon advertising can be picked up by other Bluetooth LE devices such as smartphones, WiFi gateways to send to a server and single board computers such as the Raspberry Pi.
The key features are:
- Low power and hence can work for up to years on battery power
- Interoperability with a large number of other Bluetooth LE devices
- The underlying Bluetooth LE protocol is resilient to electrical interference
- Sensing without the need for soldering or custom electronics
To learn more about the physical aspects of beacons and the actual advertising, see our article on What are Beacons?
Read more about beacons for IoT sensing.
Wireshark Supports Bluetooth Mesh
Wireshark has announced support for the Bluetooth Mesh Beacon, PB-ADV, Provisioning PDU and Proxy Bluetooth mesh protocols.
Wireshark is a protocol analyser that takes packets and decodes into human readable data. It’s usually used with other hardware and software as the last stage in processing captured data. For example, you can use Wireshark with the Nordic nRF sniffer, on Adafruit hardware and on Linux.
In the case of Bluetooth mesh, data packets are encrypted. In fact, data is double encrypted in that first the data is encrypted and then the packets. This means that while you can capture packets you can only see the packet types and Bluetooth mesh metadata. You won’t be able to decrypt the actual data. It’s more useful for determining the type and size of traffic for mesh traffic optimisation.
Read about Beacons and the Bluetooth Mesh
A Push for Bluetooth 5 Long Range
There’s a push by the Bluetooth SIG at the moment, promoting long range Bluetooth that appeared with Bluetooth 5 in June 2016. This is presumably because, to date, there haven’t been many long range end-user products. There aren’t many devices out there because you need Bluetooth 5 hardware at both ends of communication and existing devices can’t be upgraded.
Device manufacturers have been waiting for the ‘device at the other end of the communication’ (beacons, sensors, smartphones, single board computers) to become compatible before creating new products using Bluetooth 5 which is a chicken and egg situation. There are also tradeoffs around backwards compatibility and battery power. It’s more complex to create a device that supports Bluetooth 5 and is backwards compatible with Bluetooth 4. Advertising both at the same time uses more power and hence reduces the battery lifetime.
In order to validate Bluetooth 5’s long range claims, Nordic have a new blog post testing long range. The post gives a good explanation of path loss, outside vs inside and deterioration of the signal due to precipitation, humidity and reflected signals. Nordic also have an older post comparing the range of BLE, ZigBee and Thread Protocols.
iBeacons for Android, iBeacons for iOS
We often gets asked what are the best beacons for iOS and/or Android. As mentioned in our post on Which Beacons Are The Most Compatible, all beacons, whether iBeacon or Eddystone, are compatible with iOS and Android.
The universal compatibility comes about because all beacons are slight derivations of a few standard circuit designs and firmware provided by Texas Instruments, Dialog and Nordic who produce the System On a Chip (SoC) inside beacons.
Instead, you should be looking at more physical aspects such as battery size, battery life, range, on-off buttons, waterproofing and included sensors.

