A new paper is the result of collaboration between Spanish and Italian university researchers. It surveys publicly available datasets for indoor localisation, with a focus on machine learning approaches that make use of the sensors embedded in smartphones. It reviews twenty datasets released between 2014 and 2024, noting the growing trend towards multi-sensor data collection, not only Wi-Fi and Bluetooth but also accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers and other signals.
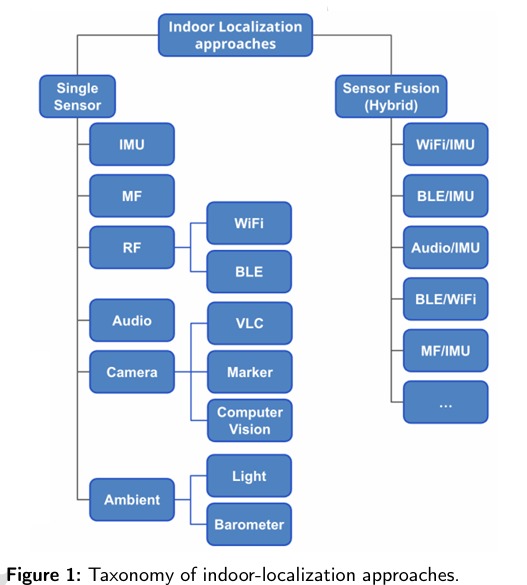
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), features prominently throughout the survey. It is identified alongside Wi-Fi as one of the most widely used technologies for radio frequency-based localisation, relying on received signal strength from Bluetooth beacons to triangulate or fingerprint positions. Several datasets in the survey focus on BLE signals, in the form of iBeacons deployed within controlled environments such as university buildings or libraries.
The review also discusses hybrid approaches, where BLE data is combined with other signals such as inertial measurements or geomagnetic readings, to improve robustness and accuracy. Machine learning techniques are highlighted as particularly effective in handling the noisy and fluctuating nature of Bluetooth signals in complex indoor environments. Some studies combine BLE with Wi-Fi fingerprints in unified models, enhancing resilience against signal drift.
In conclusion, the survey underscores Bluetooth’s importance as a practical, widely deployed technology in indoor localisation research, while also pointing out the limitations of current BLE datasets in terms of scale, diversity of environments, and long-term variability.