There’s new research from University of Catania, Italy on A Perspective on Passive Human Sensing with Bluetooth. The research identifies and discusses the factors and operating conditions that can result in varying accuracy.
The paper explains the advantages of Bluetooth over WiFi for passive human sensing. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of RFID, VLC, LoRa and LTE. The paper seeks to address the lack of search papers on considering Bluetooth as opposed to WiFi for detecting human presence.
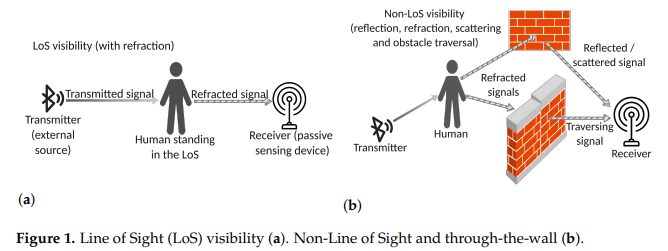
The paper describes how human presence can influence a wireless signal and covers Bluetooth Direction Finding. It explains how Bluetooth is better suited for human detection because it is less subject to electromagnetic noise.
It’s mentioned how signals received on different Bluetooth different channels have different noise and attenuation characteristics:
“Another issue often highlighted in the literature is the impossibility of independently extracting the RSSI signal values from each advertising channel of the BLE beacons. The BLE beacons need to be modified at the hardware or firmware level in order to transmit on a certain preset channel and to allow the researcher to discriminate the variation in the signal due to the presence of a human body from other fading effects.”
What isn’t mentioned in the paper is that Bluetooth Direction Finding requires analysis of the IQ data rather than RSSI. This IQ data also varies depending on the Bluetooth channel. Direction finding receivers can (and must) independently extract and process the channel specific data.